Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
iPET device creation#
This is an example how to create a new device. In this case a new system for EasyCT The device should be run only one time to create a new device. A folder with a unique identifier will be created Afterwars the device can be read from the folder and added to the new TOR files created
# # sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_path = ‘examples/EasyPETCT/easyPETCT.png’
Imports to create the device
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from scipy.optimize import curve_fit
from toor.Geometry.easyPETBased import EasyCTGeometry
# from toor.DetectionLayout.RadiationProducer import GenericRadiativeSource
from toor.DetectionLayout.Modules import PETModule, easyPETModule
from toor.Designer import DeviceDesignerStandalone
from toor.Device import StoreDeviceInFo, EnergyResolutionFunction
# from toor.TORFilesReader import ToRFile
SYSTEM ENERGY RESPONSE FUNCTION (Not mandatory)
def systemEnergyResponseFunction(E, Er, p1, p2):
"""
Energy response function of the system
:param energy: energy of the photon
:param Er: energy resolution
"""
fwhm = np.sqrt((p1 / E) ** 2 + (p2) ** 2)
return fwhm / E
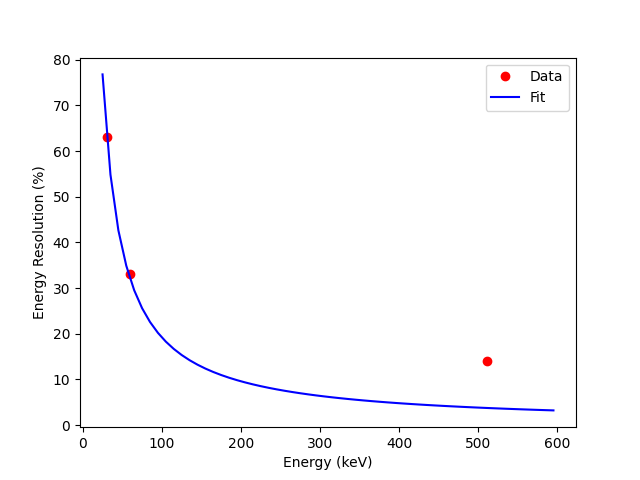
energies = np.array([30, 59.6, 511])
energy_resolution = np.array([0.63, 0.33, 0.14])
fit = curve_fit(systemEnergyResponseFunction, energies, energy_resolution)
plt.figure()
plt.plot(energies, energy_resolution * 100, 'ro', label='Data')
plt.plot(np.arange(25, 600, 10), systemEnergyResponseFunction(np.arange(25, 600, 10), *fit[0]) * 100, 'b-', label='Fit')
plt.xlabel('Energy (keV)')
plt.ylabel('Energy Resolution (%)')
plt.legend()
plt.savefig("../../images/system_energy_response_function.png")
# .. image:: ../../images/system_energy_response_function.png
# :alt: EasyCT Diagram
# :width: 400px
# :align: center
energy_window = [energies - energies * systemEnergyResponseFunction(energies, *fit[0]),
energies + energies * systemEnergyResponseFunction(energies, *fit[0])]
systemEnergyResolution = EnergyResolutionFunction(p1=fit[0][1], p2=fit[0][2])
C:\Users\pedro\OneDrive\Documentos\GitHub\Infinity-Tomographic-Reconstruction\docs\source\examples\iPET\1_Device_creation.py:60: OptimizeWarning: Covariance of the parameters could not be estimated
fit = curve_fit(systemEnergyResponseFunction, energies, energy_resolution)
Setup the type of the detector module. You should not call the PETModule class directly. This object should entry as argument in the geometry class type for proper setting. This allows to set multiple cells. Number of modules, rotations and translations are set after the geometry class is created.
_module = PETModule
# _module = DualRotationModule
The next step is to choose the geometry type, which is DualRotationCTGeometry in this case. This function is inherited from the DualRotationGeometry class which is an Device Object. Here we set the distance between the two points of rotation, the distance between the fan motor and the detector modules (closest side) and the distance between the fan motor and the detector modules (far side). as well as the initial position of the x-ray source.
newDevice = EasyCTGeometry(detector_moduleA=_module, detector_moduleB=_module)
newDevice.setDeviceName("iPET")
newDevice.setDeviceType("PET")
newDevice.setEnergyResolutionFunction(systemEnergyResolution) # use to apply energy cuts
newDevice.setDistanceBetweenMotors(65) # Distance between the two points of rotation
newDevice.setDistanceFanMotorToDetectorModulesOnSideA(
0) # Distance between the fan motor and the detector modules (closest side)
newDevice.setDistanceFanMotorToDetectorModulesOnSideB(
130) # Distance between the fan motor and the detector modules (far side)
# newDevice.xRayProducer.setFocalSpotInitialPositionWKSystem([12.55, 3, 0])
# newDevice.evaluateInitialSourcePosition() # evaluate the initial position of the source
Set modules Side A. For each module, should be in the list the equivalent rotation and translation variables. If for example two modules are set, the variables should be in the list as follows:
moduleSideA_X_translation = np.array([15, 20], dtype=np.float32) moduleSideA_Y_translation = np.array([0, 0], dtype=np.float32)
…
Very important. The translations are regarding the fan motor center. The rotations are regarding the center of the module.
newDevice.setNumberOfDetectorModulesSideA(4)
moduleSideA_X_translation = np.array([10,10,10,10], dtype=np.float32)
moduleSideA_Y_translation = np.array([0,0, 0, 0], dtype=np.float32)
moduleSideA_Z_translation = np.arange(0,16*1.6*4+3,16*1.6+1)
moduleSideA_alpha_rotation = np.array([0,0,0,0], dtype=np.float32)
moduleSideA_beta_rotation = np.array([0, 0, 0, 0 ], dtype=np.float32)
moduleSideA_sigma_rotation = np.array([0,0,0,0], dtype=np.float32)
for i in range(newDevice.numberOfDetectorModulesSideA):
# newDevice.detectorModulesSideA[i].model32()
# newDevice.detectorModulesSideA[i].model16_2()
newDevice.detectorModulesSideA[i].setXTranslation(moduleSideA_X_translation[i])
newDevice.detectorModulesSideA[i].setYTranslation(moduleSideA_Y_translation[i])
newDevice.detectorModulesSideA[i].setZTranslation(moduleSideA_Z_translation[i])
newDevice.detectorModulesSideA[i].setAlphaRotation(moduleSideA_alpha_rotation[i])
newDevice.detectorModulesSideA[i].setBetaRotation(moduleSideA_beta_rotation[i])
newDevice.detectorModulesSideA[i].setSigmaRotation(moduleSideA_sigma_rotation[i])
Set modules Side B.
newDevice.setNumberOfDetectorModulesSideB(4)
moduleSideB_X_translation = np.array([-140, -140, -140, -140], dtype=np.float32)
moduleSideB_Y_translation = np.array([0, 0, 0,0], dtype=np.float32)
moduleSideB_Z_translation = np.arange(0,16*1.6*4+3,16*1.6+1)
moduleSideB_alpha_rotation = np.array([-0, -0, -0, -0 ], dtype=np.float32)
moduleSideB_beta_rotation = np.array([0, 0, 0, 0 ], dtype=np.float32)
moduleSideB_sigma_rotation = np.array([180,180,180,180], dtype=np.float32)
for i in range(newDevice.numberOfDetectorModulesSideB):
# newDevice.detectorModulesSideB[i].model32()
# newDevice.detectorModulesSideB[i].model16_2()
newDevice.detectorModulesSideB[i].setXTranslation(moduleSideB_X_translation[i])
newDevice.detectorModulesSideB[i].setYTranslation(moduleSideB_Y_translation[i])
newDevice.detectorModulesSideB[i].setZTranslation(moduleSideB_Z_translation[i])
newDevice.detectorModulesSideB[i].setAlphaRotation(moduleSideB_alpha_rotation[i])
newDevice.detectorModulesSideB[i].setBetaRotation(moduleSideB_beta_rotation[i])
newDevice.detectorModulesSideB[i].setSigmaRotation(moduleSideB_sigma_rotation[i])
Set the inital coordinates of the system. In both coordinate
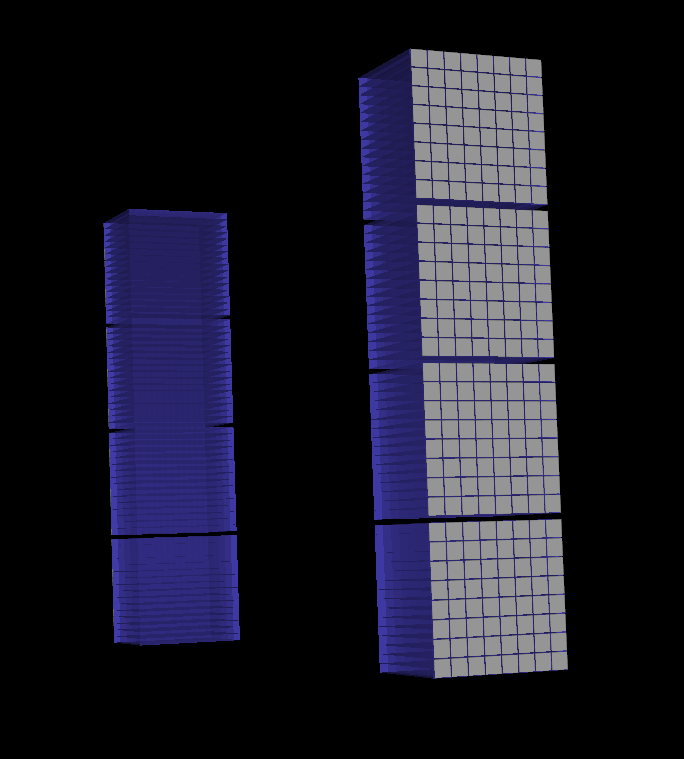
newDevice.generateInitialCoordinatesWKSystem()
# newDevice.generateInitialCoordinatesXYSystem()
Save the device in a folder with a unique identifier. The folder will be created in the current directory.
modifyDevice = False
if not modifyDevice:
newDevice.generateDeviceUUID() # one time only
newDevice.createDirectory() # one time only
storeDevice = StoreDeviceInFo(device_directory=newDevice.deviceDirectory) # one time only
device_path = newDevice.deviceDirectory
else:
device_path = "C:\\Users\\pedro\\OneDrive\\Documentos\\GitHub\\Infinity-Tomographic-Reconstruction\\configurations\\08d98d7f-a3c1-4cdf-a037-54655c7bdbb7_EasyCT"
storeDevice = StoreDeviceInFo(device_directory=device_path) # one time only
storeDevice.createDeviceInDirectory(object=newDevice)
Device created successfully
readDevice = StoreDeviceInFo(device_directory=device_path) # read the device saved
newDevice_Read = readDevice.readDeviceFromDirectory()
designer = DeviceDesignerStandalone(device=newDevice)
designer.addDevice()
# designer.addxRayProducerSource()
designer.startRender()
Test some initial positions of the source and the detectors
unique_header = np.repeat(np.arange(0, 32), 13)
axial_motor_angles = (np.zeros(32 * 13))
fan_motor_angles = np.tile(np.arange(-90, 105, 15), 32)
Total running time of the script: (8 minutes 34.839 seconds)